Complete Profiling of Procainamide Labeled Human IgG N-Glycans using UHPLC Coupled with an Orbitrap-based Mass Spectrometer
July 07, 2020
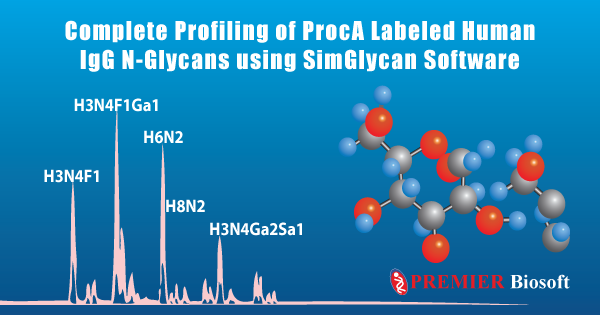
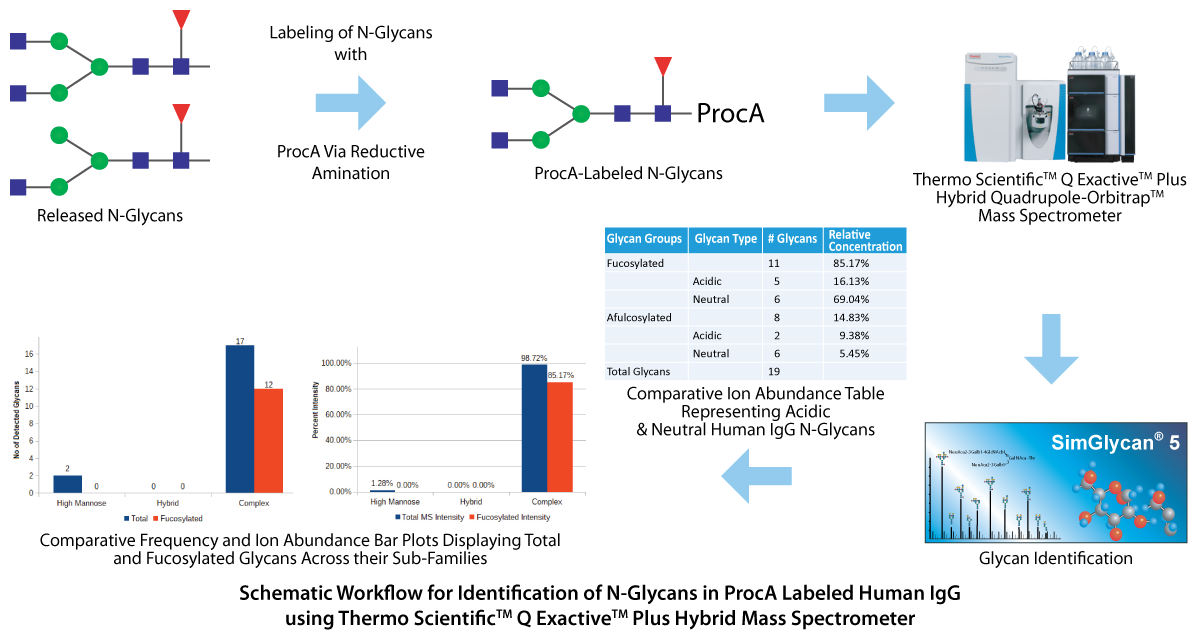
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) comprises almost three fourth of serum antibodies in humans. Checking of IgG levels is one of the most common clinical approaches to measure an individual's immunity for specific pathogens. Glycosylated IgGs are considered to have a profound impact on the role of therapeutic antibodies mainly during antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Comprehensive N-glycan profiling of IgGs is needed for a better understanding of their role. A hyphenated technique Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) coupled with an Orbitrap-based mass spectrometer (MS) was used to identify N-glycans in the procainamide (ProcA) labeled Human IgG.
The raw data files corresponding to four technical replicates of hIgG samples were analyzed using SimGlycan software. The processing of LC-MS and tandem MS (MS/MS) data was performed using predefined parameters to generate LC compounds clustered with MS/MS spectra. An MS/MS database search was conducted on the detected compounds using 5 ppm error tolerance for both precursor and product ions. To reduce false positives, only those glycan structures are included in the final list that had 80% of their monosaccharide residues explained by structure-specific characteristic ions in the MS/MS spectra. A total of 23 unique glycans were identified. A comparative glycan profiling based on fucosylation and glycan type (Acidic or Neutral) was performed using Microsoft Excel. For more details, please visit our poster.
| Comment | Share |
|


