Shotgun Lipidomics of Prostate Cancer Cells using Shimadzu LC/MS 8050 Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer and Simplified Data Analysis by SimLipid® Software
September 20, 2017
Lipidomics is an emerging field in biomedical research as lipids play an important role in cell, tissue and organ physiology and have potential as biomarkers of disease or treatment success. Lipidomics has also been widely studied in many areas including prostate cancer research, e.g., identification of lipid species in bio-fluids as biomarkers in diagnosis of prostate cancer with high sensitivity.
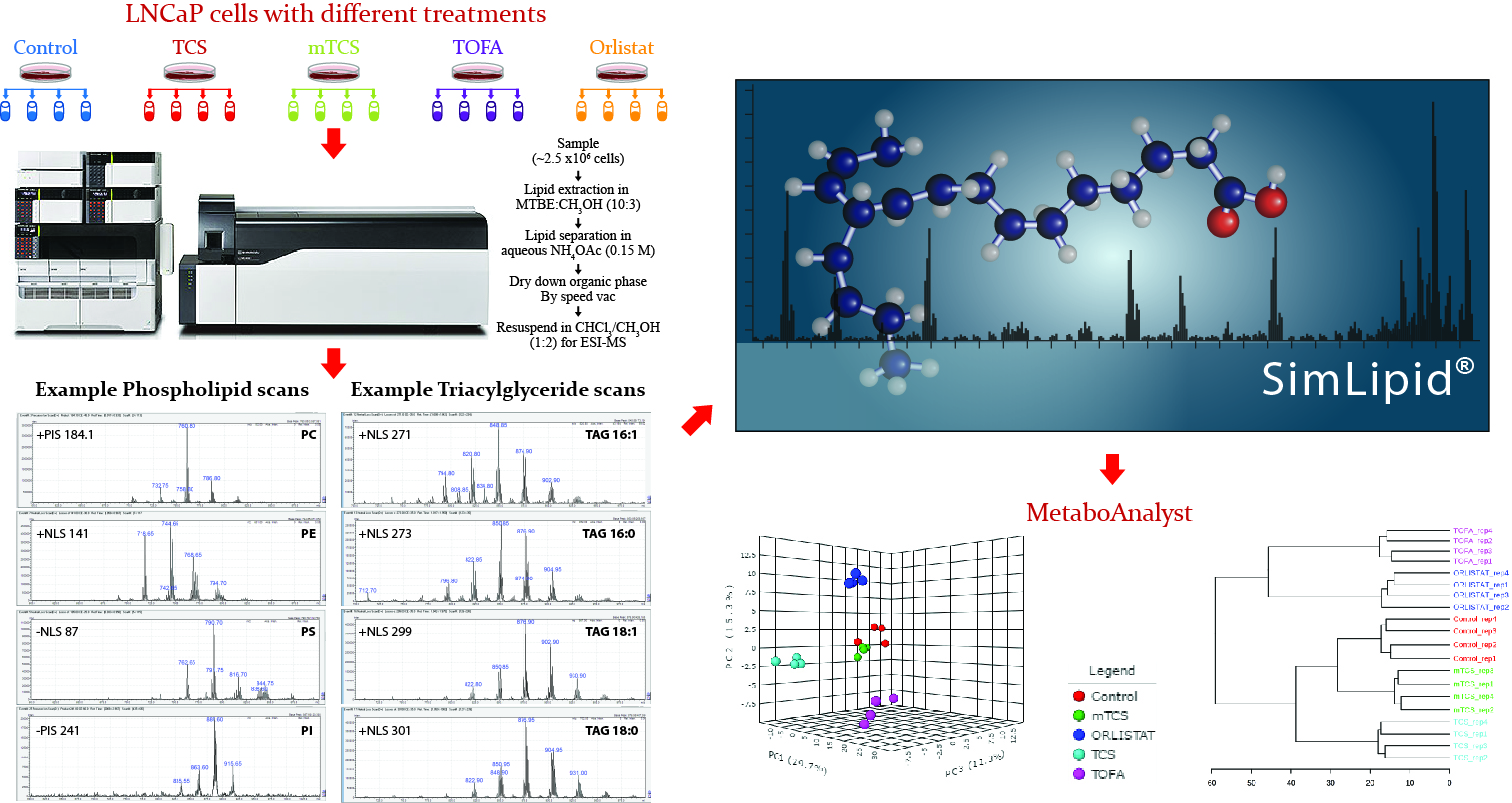
Shotgun lipidomics involves identification and quantification of lipids by direct infusion of complex lipid samples into the mass spectrometer without any chromatographic separation. In this study, we investigate the details of lipid compositions difference between prostate cancer patients treated with different drugs and the control group.
Brief description of the method: ESI based direct infusion method was used for quantitative lipidomics analysis of LNCaP cells with different treatments. Data was acquired following Precursor Ion/Neutral Loss Scanning (PIS/NLS) experiments using Shimadzu LC/MS 8050 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (http://www.shimadzu.com, Kyoto, Japan). High Throughput data analysis was performed using SimLipid v. 6.0 software (www.premierbiosoft.com, Palo Alto, USA) showing promising functionality for both qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Statistical analysis – hierarchical cluster analysis, and principal component analysis (PCA) - using MetaboAnalyst software was done that clearly separated the study groups and stratified different treatments.
| Comment | Share |
|


