Home >> Blog >> Study of Breast Cancer Metastasis using SFC MS and DIA FIA MS with SimLipid Software
Fast Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC) Separation and Shotgun Lipidomics with High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS) for the Study of Breast Cancer Metastasis
March 02, 2020
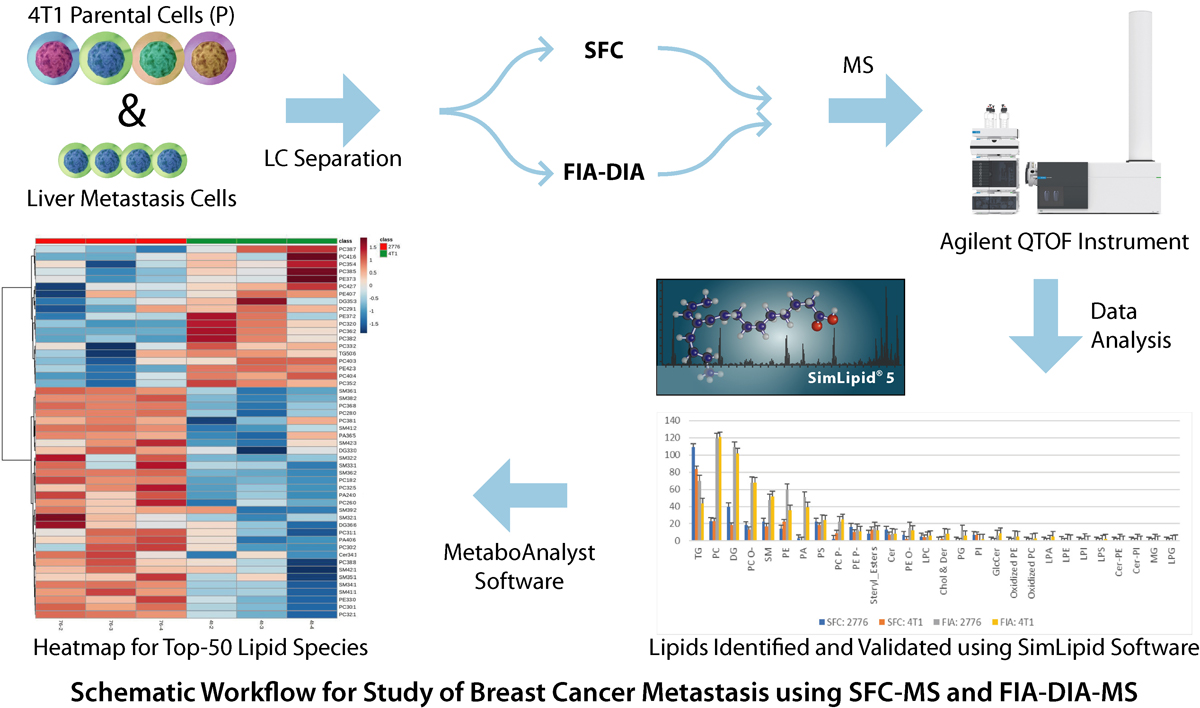
Metabolic reprogramming allows breast cancer cells to adapt to different metastatic sites using different pathways based on the tissue site. Understanding these metabolic adaptations is vital in the study of breast cancer metastasis. 4T1 murine breast cancer cells, a highly aggressive model, was chosen for this study because 4T1 cells can spread to lymph nodes, bones, lungs, liver and brain. Lipid adaptations were studied between liver-metastatic and parental 4T1 cells using supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry.
Four replicate samples were separated using both techniques-SFC and flow injection analysis (FIA) with data independent acquisition (DIA) and analyzed using Agilent QTOF instrument. The data was processed using SimLipid software. A total of 1173 and 1054 lipids were initially identified for liver-specific and 4T1 cancer cells respectively. Later, these lipids were validated using their corresponding head group diagnostic ions observed in MS/MS spectra e.g., 184.073 m/z for phosphocholines, neutral loss of 141 from parent ion mass for phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) lipids. Also, DG and TG were identified with at least 1/2 of the 2/3 fatty acid chains. 836 and 654 lipids were further annotated for liver-metastatic and 4T1 cells respectively.
For comparison of these two groups of samples, MetaboAnalyst software was used for performing statistical analysis. Based on these results, PE was enhanced in liver-metastatic in comparison to 4T1 cells. Also, the PE-O was identified as higher within these PEs. Among other lipid categories, triacyl glycerides (TG) and phosphotidic acids (PA) in the liver-metastatic cells were higher in expression. Both samples separated with SFC as well as the shotgun FIA showed this trend. Based on these results, an efficient workflow for performing lipid profiling using SFC-MS and FIA-MS was shown below. The pilot study described here provides an understanding of changes in complex lipid biochemistry between highly aggressive and non-specific (4T1) compared to the highly specific liver-metastatic cells. For more details, please visit here.
| Comment | Share |
|


