References >> MLPA®
MLPA® ProbesIntroduction to MLPA® or Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification
MLPA® (Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification) is a simple, high throughput and easy to perform method developed by MRC Holland that allows detection of DNA copy number changes of up to 40 sequences in a single reaction. This relatively simple technique is based on the semi-quantitative polymerase chain reaction principle and can be applied for detecting copy number changes and methylation quantification of the genomic DNA or for mRNA profiling.
Structure of an MLPA® Probe
MLPA® Probes are of Two Types:
- Probes containing one synthetic and one M-13 derived probe oligonucleotide. The probes result in producing an amplification product between 130 and 481 nucleotides.
- Probes containing two synthetic oligonucleotide probes. The probes result in producing an amplification product between 94 and 130 nucleotides. These probes do not have a stuffer sequence.
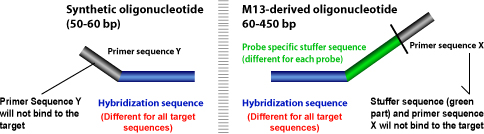

MLPA® Probe Chemistry
MLPA® probes consist of two oligonucleotides, each containing a PCR primer sequence and a sequence complementary to the target, known as the hybridization sequence.
The two probes hybridize immediately adjacent to each other. When the probes correctly hybridize to the target sequence they are ligated by a thermo stable ligase enzyme. The PCR primers exponentially amplify the ligated probes. One of the primers is labeled with a fluorescent dye to visualize the amplification product of the probe. MLPA® based detection assays can be run in a single tube as non-ligated probes do not need to be removed.
Sequence type electrophoresis is used to separate the resulting PCR products. Each MLPA® probe length is designed such that it can be easily identified when the amplification product of the PCR is run through a gel. The difference in size is achieved with the help of the stuffer sequence.
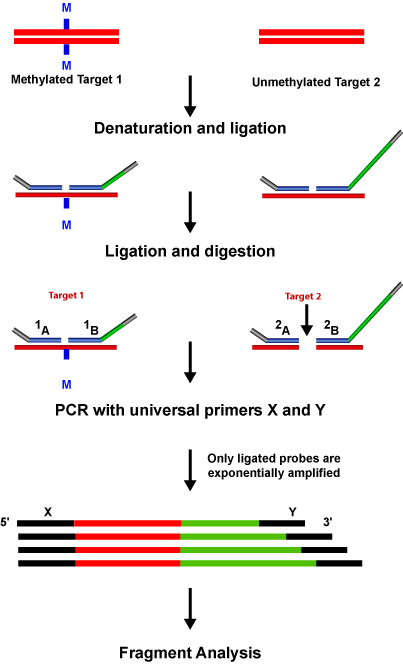
Steps in Performing MLPA® Based Detection with Synthetic MLPA® Probes
- Denaturation
Sample genomic DNA is denatured at a temperature of 98°C.
- Hybridization and Ligation
The MLPA® probe mix is added to the denatured genomic DNA. Both the oligonucleotides hybridize to the target sequence. Then the probes are ligated by a thermostable ligase.
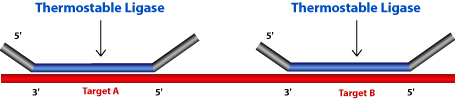
- Amplification
A universal primer pair is used to amplify all the ligated probes. Then a small amount of reaction mix containing dNTPs, Taq polymerase and one unlabeled and one labeled PCR primer is added. The primers are complementary to the universal primer sequences of the MLPA® probes. Each MLPA® probe is designed to have a specific size so that when the amplification products of the PCR are run on a gel, the product of each probe can be identified by its size. The MLPA® procedure requires a thermocycler and standard sequencing equipment for identification and quantification of the amplification products. The tricky part is the design of MLPA® probes.
Applications of MLPA® Technique
- Detecting Gene Copy Number: Gene Copy Number refers to the number of copies of a particular gene in the genotype of an individual. MLPA® technique can be used to establish the copy number of up to 40 nucleic acid sequences in a single reaction. The copy number changes are important to understand. They are the primary cause of increase or decrease in the expression of the protein that a gene encodes.
- MLPA® technique can be used for quantitative detection of genomic deletions, duplications and point mutations. MLPA® discriminates sequences that differ even by a single nucleotide and can be used to detect known mutations. Only the perfectly matched probes ligate.
- DNA Methylation Analysis & mRNA Profiling: Aberrant methylation of CpG islands has been known to be associated with the transcriptional inactivation of the tumor suppressor genes in human cancers. MLPA® allows detection of the methylation status of up to 40 sequences in a single reaction.
Design Parameters for Synthetic MLPA® Probes
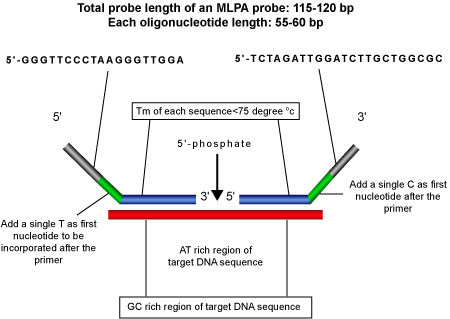
Length Criteria: Length of the hybridization sequence should be greater than 21 bases and the two hybridization sequence should be adjacent to each other.
-
Amplicon Length: The designed probes should have a unique amplicon length.
-
Tm Criteria: Tm of the probes should be 72 +/- 5 °C.
-
Avoid Homology: The designed probes should be unique. Homologous regions should be avoided by performing a BLAST search.
-
Secondary Structures: The designed probes should be tested for hairpins, self dimer, runs. Ideally the probe should have as few secondary structures as possible.
-
Unique Ligation Site: To avoid mispriming, the ligation site and the surrounding nucleotides should be non-homologous to all the selected sequences.
-
Nucleotide Following the PCR Primer: First nucleotide following the PCR primer sequence should, preferably, not be adenine as it results in low peak size for the probe amplification product.
- Probe Specificity: For highest specificity, both the oligonucleotides should have an AT rich region around the ligation site and a CG rich region adjacent to it.
MLPA® Probe Design Software
Advantages of the MLPA® Technique
MLPA® is a variation of the polymerase chain reaction. It facilitates the amplification and detection of multiple targets with a single primer pair. In a standard multiplex PCR reaction, each fragment needs a unique amplifying primer pair. These primers being present in a large quantity result in various problems such as dimerization and false priming. With MLPA®, one does not amplify the target DNA, but only the probes. Thus, many sequences (upto 40) can be amplified and quantified using just a single primer pair. Compared to other techniques, MLPA® reaction is fast, cheap and very simple to perform.
Software for Designing MLPA® Probes
AlleleID® is a comprehensive tool co-developed with MRC-Holland to design highly specific oligos for MLPA® assays. Learn more about AlleleID®.


