Bioinformatics Tool for Mass Spectrometry Based Lipidomics Workflows
April 26, 2018
The main biological functions of lipids include energy storage, acting as structural components of cell membranes, and participating as important signaling molecules. Lipids play diverse and important roles in nutrition and health e.g., abnormal levels of certain lipids, particularly cholesterol, and trans fatty acids are risk factors for heart disease and other diseases. Lipids also play a key role in cell, tissue and organ physiology with diseases such as cancer and diabetes which involve disruption of metabolic enzyme pathways.
Comparative studies of complex lipid mixtures found in cells and tissues could potentially reveal lipid biomarkers, as the presence of lipids in membranes or as signaling molecules is reflective of the physiological state of an organism at a given time.
Advancements in analytical methods, especially liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry, led to the development of lipid profiling methods. It may be noted that a single analytical method to screen all lipids in a biological system has yet to be developed. Targeted and non-targeted approaches based on chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) are employed for such studies. Both the approaches involve identification and measurement of lipids in samples.
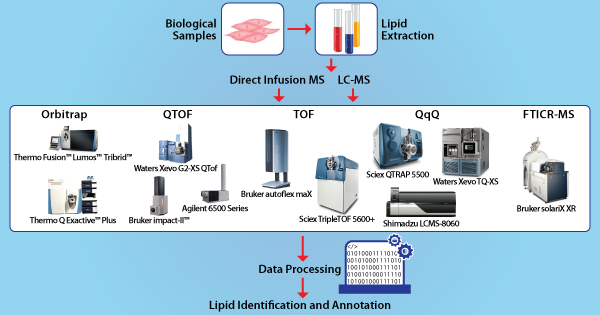
One of the major challenges with MS based lipidomics analysis is the chemical complexity and the variation in concentration of thousands of lipid species that are present in biological samples. Automated interpretation of lipid MS/MS spectra is more challenging as compared to other biopolymers such as DNA, carbohydrates or peptides. Identification of lipids requires sophisticated analysis since lipids show much less standardized fragment mass spectra. Each lipid class has its own fragmentation patterns as well as ionization efficiency. The use of shotgun-, LC-, MALDI- MS and MS/MS lipidomics workflows for targeted and non-targeted approaches necessitates the use of multiple algorithmic and software analysis approaches to automate data analysis.
SimLipid software enables users to analyze lipidomics data generated by above mentioned MS-based workflows. The program can read raw data directly from native file formats of major MS instruments manufacturing vendors, annotate the identified lipids and quantify them.
View the list of MS based lipidomics workflows supported by SimLipid software.
| Comment | Share |
|


