A high throughput informatics tool for identification and relative quantitation of lipids using data from LC-, MALDI-, Shotgun-, Mass Spectrometry Workflows
The main biological functions of lipids include energy storage, acting as structural components of cell membranes, and participating as important signaling molecules.
Comparative studies of complex lipid mixtures found in cells and tissues could potentially reveal lipid biomarkers. The presence of lipids in membranes is reflective of the physiological state of an organism at a given time. Targeted and non-targeted approaches based on chromatography and mass spectrometry are employed for such studies. Both the approaches involve identification and measurement of lipids in the samples.
The challenges with mass spectrometry based lipidomics are the chemical complexity and large range of concentration of thousands of lipid species that are present in biological samples. Moreover, identification of lipids requires sophisticated software since automated interpretation of lipid MS/MS spectra is more challenging as compared to other biopolymers such as DNA, carbohydrates or peptides since lipids show much less standardized fragment mass spectra. Each lipid class has its own fragmentation patterns as well as ionization efficiency.
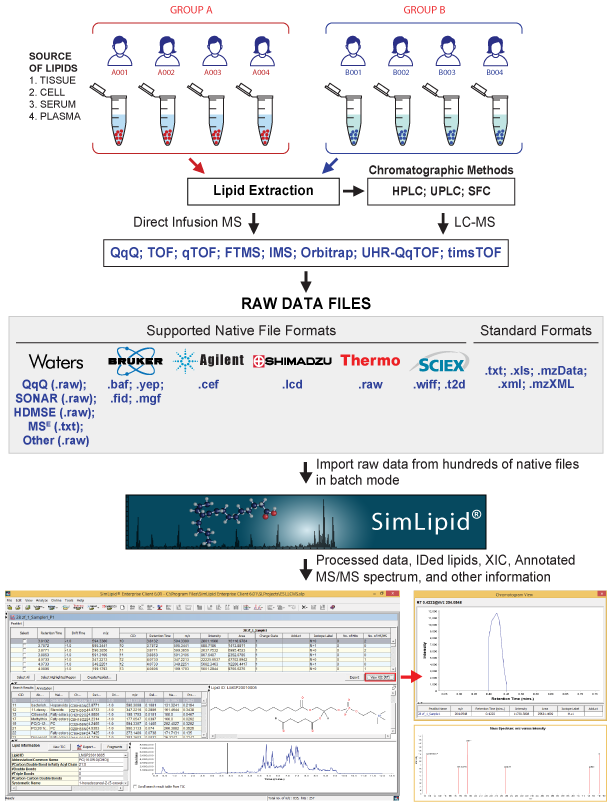
SimLipid® is a high throughput lipid identification and quantification software. It can process raw data from hundreds of LC-MS and MS/MS experimental runs for LC-peak detection, peak-picking, molecular feature finding and retention time alignment. The raw data or peaklists – dataset containing processed LC-MS data – can be subjected to MS and MS/MS database search for structural elucidation, even in batch mode. A proprietary scoring mechanism distinguishes isobaric candidate structures for each MS/MS scan. The SimLipid Database contains 40,312 lipids, and 1,508,293 structure-specific in-silico MS/MS characteristic ions. Besides this, the database also stores 5,227 transitions of precursor ion scan and neutral loss scan triple quadrupole mass spectrometry methods corresponding to 1,179,393 and 221 unique fatty acyls from glycerophospholipids, glycerolipids, and sphingolipids respectively.
Finally, for the identified peaks, correction of experimental peak intensities (for their isotopic overlaps) can be performed in batch mode. Relative quantification of the profiled lipids based on user-specified internal standards can also be performed.
What Our Customer Say About Us
"I used SimLipid and found it quite useful in analyzing lipids. The software provides valuable and detailed lipid information which makes it easy to study lipid data."
-Ms. Piyachat Chansela, Hamamatsu University, JapanThe program accepts raw data in:
(I) standard data file formats namely,
- text, MS Excel, mzData, and mzXML;
(II) vendor-specific native data file formats namely,
- .raw from Waters Corporation native files for DDA , QqQ methods,
- .lcd from Shimadzu Corporation,
- .fid, *.baf and *.yep from Bruker Daltonics,
- .wiff, and .t2d from SCIEX
- .raw from Thermo Fisher Scientific™, and
- .cef from Agilent Technologies
The software enables lipid identification and profiling by searching observed precursors and product ions, retention times and other taxonomy based filters against known lipid structures available in the SimLipid® database. Additional information such as lipid ID, lipid abbreviation, systematic name, composition and other database links are also made available for easy reference.